Home

WarmUp

What is Physics Good
For?
Puzzle
Lab Prep

Course Information

Communications
Homework Server
|
 |
Sample Final exam for PHY251
| Questions (10 points each):
Please blacken the letter of the best answer
for each question. |
|
Q1 An ideal 10 V battery connected
across a resistor generates 1000 J in 20
seconds. The value of the resistor is
a) 1 Ohm.
b) 2 Ohms.
c) 50 Ohms.
d) 100 Ohms. |
Q2 A parallel plate capacitor is
connected to a battery until it is fully
charged, it is then disconnected, and the
plates are pulled apart such that their
separation is doubled. Which of the following
statements is true?
a) The charge on the capacitor and the energy
stored in it both increase.
b) The charge increases but the energy remains
the same.
c) The energy increases but the charge remains
the same.
d) The charge and the energy both remain the
same. |
|
Q3 A wire carries 10 amps from north
to south. An electron is located directly below
the wire and is traveling straight up. The
force on the electron is
a) To the North
b) To the South
c) To the East
d) To the West
e) Zero
f) None of the above |
Q4 For a circuit design, an engineer
wants to choose an inductor that will store 30
mJ of energy when it is carries a current of 5
A. What value inductor should she use?
a) 1.5 mH
b) 2.4 mH
c) 4.0 mH
d) 6.7 mH
e) None of the above
|
|
Q5 A heat engine operating between
27 °C and 327 °C is 3/4 as efficient as
a Carnot engine operating between the same
temperatures. Its efficiency is
a) 6%
b) 69%
c) 38%
d) 50% |
Q6 In process #1, two moles of a
diatomic ideal gas at room temperature and one
atmosphere are heated to a temperature of 600 K
at constant pressure. In process #2, two moles
of the same gas at the same initial conditions
are heated to 600 K at constant volume. Which
of the following is true?
a) Process #1 requires more heat
b) Process #2 requires more heat
c) The two processes require the same amount
of heat
d) There is not enough information to decide
which process requires more heat |
|
| Thermodynamics Problems (40 ponts each):
Please do 2 of the following 3 problems. You
must show your work. Credit will be awarded
only for answers accompanied by correct
work. |
|
P1 An 0.1 kg copper vessel at 90
°C contains 1.8 kg of water, also at 90
°C. A piece of ice of mass 0.3 kg at
T=-20 °C is added and the container
is sealed.
Please find the final temperature of the
system.
Useful data:
The specific heat of copper is 390
J/kg-K
The specific heat of water is 4190 J/kg-K
The specific heat of ice is 2000 J/kg-K
The latent heat of fusion of water is 334,000
J/kg
The latent heat of vaporization of water is
2,256,000 J/kg
|
|
P2 3.5 moles of a monatomic ideal
gas are at P = 3.5 x 105 Pa
in a volume of 0.025 m3. The gas
expands adiabatically to 0.05 m3.
Please find
a) The initial and final temperature of the
gas.
b) The change in internal energy of the
gas.
c) The final pressure of the gas.
d) The work done by the gas. |
|
P3 Three moles of an ideal diatomic
gas begin at volume V = 0.065
m3 and 1 atmosphere. The gas is
taken through the following cycle.
- Volume doubled at constant
pressure
- Pressure reduced by a factor
of two at constant volume
- Volume reduced by a factor of
two at constant pressure
- Pressure doubled at constant
volume
a) Draw a P-V diagram for this cycle
b) Calculate the heat, work, and change in
internal energy for each of the four
processes.
c) Calculate the total heat, work, and change in internal energy for the whole cycle.
|
|
| Other Problems (40 ponts each): Please do 4
of the following 5 problems. You must show your
work. Credit will be awarded only for answers
accompanied by correct work. |
|
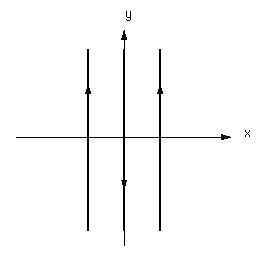 P4 Three
parallel wires carry currents of I1,
-2I1, and I1. The wires
are located in the x-y plane, and run parallel
to the y axis at x = -1, 0, and 1 as shown in
the figure. P4 Three
parallel wires carry currents of I1,
-2I1, and I1. The wires
are located in the x-y plane, and run parallel
to the y axis at x = -1, 0, and 1 as shown in
the figure.
a) Give an expression for the magnetic field
to the right of all the wires (x greater than
1).
b) Give an expression for the force per meter
on the wire at x = -1. |
|
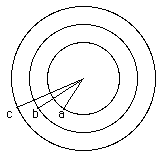 P5 A solid
insulating sphere of radius a carries a
total charge Q as a uniform charge density (rho
= Q/V = Q/(4/3)pi
a3. Concentric with this
sphere is a conducting spherical shell with
inner radius b and outer radius
c. The conducting shell carries a charge
2Q. P5 A solid
insulating sphere of radius a carries a
total charge Q as a uniform charge density (rho
= Q/V = Q/(4/3)pi
a3. Concentric with this
sphere is a conducting spherical shell with
inner radius b and outer radius
c. The conducting shell carries a charge
2Q.
a) Find the electric field in each of the
regions: r less than a, r between a and b, r
between b and c, and r greater than c.
b) Find the surface charge density on the
inner and outer surfaces of the spherical
shell.
c) Find the potential differnce between the
outer surface of the sphere and the inner
surface of the shell. |
|
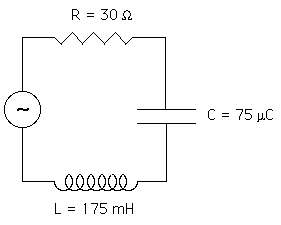
P6 Consider a series RLC circuit. The
source supplies a current of I=15cos(120
 t) amperes. The values of the circuit
elements are R = 30 Ohms, L =
175 mH, and C = 75 microfarads. t) amperes. The values of the circuit
elements are R = 30 Ohms, L =
175 mH, and C = 75 microfarads.
Please find
- The capacitive reactance
- The impedance
- The phase angle between V and
I
- The average power delivered by
the source.
- The maximum energy stored in
the inductor
|
|
P7 A small styrofoam sphere of mass
0.2 g and charge 0.6  C is
initially at rest at the origin. At t = 0, an
electric field of magnitude 200 V/m is
applied directed in the z-direction. After
two seconds, the field is shut off. C is
initially at rest at the origin. At t = 0, an
electric field of magnitude 200 V/m is
applied directed in the z-direction. After
two seconds, the field is shut off.
You may ignore gravity and air resistance.
Please answer the following questions.
- What is the acceleration of
the charge while the field is turned
on?
- What is the location of the
charge at t = 3 seconds.
- What is the kinetic energy of
the charge at the moment the field is
turned off?
- After coasting for a while,
the charge enters a magnetic field of
magnitude 0.15 T directed in the
x-direction, what will be the radius of
curvature of the particle's path
|
|
P8 A 10 mF capacitor, a 10 V battery,
a 100 Ohm resistor and a switch are connected
in series. At t = 0, the switch is closed.
Please find
- The current just after the
switch is closed.
- The current a long time
later.
- The voltage across the
capacitor after 1 second.
- The energy stored in the
capacitor after 1 second.
|
|
| Other types of problems to look out for:
Ampere's law, Faraday's Law, dc circuits,
mirrors, lenses, prisms, the Biot-Savart law, E
fields of charge distributions, RL circuits,
and statics problems involving electric forces.
Your best guides are the problems
worked out in recitation and the test prep
problems. |
©2004-2006 IUPUI, all rights reserved.
This site is made possible by
funding from the National Science Foundation
(DUE-9981111).
|
|




