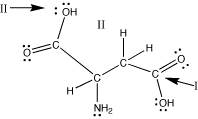
aspartic acid
|
Look at the carbon indicated
by arrow I. There are 3 electron charge clouds around it:
a single bond to oxygen, a double bond to oxygen, and a
single bond to carbon. The farthest apart 3 "things"
can be from each other is a trigonal planar arrangement
with the charge clouds 120oapart. Thus, the O-C-O
bond angle is 120o. As all of the charge clouds
are connected to atoms, the geometry around this carbon
atom is trigonal planar.
Now look at the oxygen indicated by arrow
II. There are 4 electron charge clouds around it: a single
bond to carbon, a single bond to hydrogen, and two lone
pairs of electrons. The farthest apart 4 "things"
can be is in a tetrahedral arrangement where the charge
clouds are approximately 109o apart. Thus, the
C-O-H bond angle here is about 109o. The geometry
around this oxygen is bent. (We have to think tetrahedral
for the arrangement of the electron charge clouds to determine
the bond angles. To describe the shape around this oxygen,
we look at the atoms. Since only two of the charge clouds
are atoms, the shape around this oxygen atom is described
as bent.) |
