 |
 "What is Chemistry Good For?"
"What is Chemistry Good For?"
The for-credit questions are available at the end of this page.
Please respond before 5 AM, Wednesday, December 13th, 2000.

Chemistry is Good for Supplying Gases
Liquid Air, Brrrrr-So Cold
 Gases are good for many things. A very simple, readily available gas is
nitrogen, which has the simple formula N2. It is very nonreactive,
colorless, odorless, tasteless, and has a very low boiling point.
The usefulness of nitrogen hinges on its physical properties and
lack of chemical properties. Since a nitrogen atmosphere is so
unreactive, storing metals or other chemicals in an inert nitrogen
atmosphere will prevent them from reacting and decomposing or corroding.
Foods that are stored in an inert atmosphere are protected from some
forms of spoilage. Since the boiling point of liquid nitrogen is
extremely low (-196 degrees Celcius), it is used to generate very low
temperatures. This can be used for the rapid freezing of foods like
meat patties or prepared dinners and can prevent chemical reactions from
happening altogether. Nitrogen react with hydrogen to form ammonia if
a catalyst is present. Ammonia is an integral part of the fertilizer
production process, without which there is no way that farmers could
produce enough food to feed the population of the world. Helium and
argon, which are even less reactive than nitrogen, are used for the
atmospheres in which arc welding is done. Liquid helium boils at 4K, so
a liquid helium bath can provide temperatures that are low enough for
many materials to be superconductors. The usefulness of even the least
reactive gases is impressive. The reactive gases are used to make
important materials and a variety of other chemicals.
Gases are good for many things. A very simple, readily available gas is
nitrogen, which has the simple formula N2. It is very nonreactive,
colorless, odorless, tasteless, and has a very low boiling point.
The usefulness of nitrogen hinges on its physical properties and
lack of chemical properties. Since a nitrogen atmosphere is so
unreactive, storing metals or other chemicals in an inert nitrogen
atmosphere will prevent them from reacting and decomposing or corroding.
Foods that are stored in an inert atmosphere are protected from some
forms of spoilage. Since the boiling point of liquid nitrogen is
extremely low (-196 degrees Celcius), it is used to generate very low
temperatures. This can be used for the rapid freezing of foods like
meat patties or prepared dinners and can prevent chemical reactions from
happening altogether. Nitrogen react with hydrogen to form ammonia if
a catalyst is present. Ammonia is an integral part of the fertilizer
production process, without which there is no way that farmers could
produce enough food to feed the population of the world. Helium and
argon, which are even less reactive than nitrogen, are used for the
atmospheres in which arc welding is done. Liquid helium boils at 4K, so
a liquid helium bath can provide temperatures that are low enough for
many materials to be superconductors. The usefulness of even the least
reactive gases is impressive. The reactive gases are used to make
important materials and a variety of other chemicals.

An essay that even briefly described the uses of all the known gases
would be prohibitively long, so let us just consider the production of
the gases that are present in our atmosphere, nitrogen and oxygen.
If you wanted to isolate pure oxygen, how would you do it? How much
pure oxygen is sold each year? Pure oxygen, in addition to being used
as a cryogenic fluid and an oxidant for the hydrogen that fuels the
space shuttle, is very important in the medical profession for people
who have respiratory problems. One of the leading oxygen-producing
companies isolates 5000 tons of oxygen per day. WOW!!

For a very long time, the production of oxygen gas relied on a chemical
reaction. One such reaction is the thermal decomposition of potassium
chlorate to give potassium chloride and oxygen. Producing 5000 tons of
oxygen per day would not be possible using this method. In time, as
the technology for better refrigeration processes and better compressors
was developed, this made the liquefaction of air possible. At very low
temperatures and high pressures, air can be condensed into liquid form
and then distilled to isolate the components of air in pure form. Remember
that at atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of liquid nitrogen is
-196 degrees Celcius. It is no small feat of engineering to produce
large quantities of liquid air.
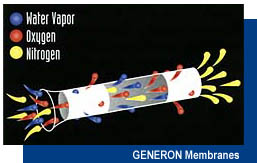
Recently, even other innovative technological processes have been
developed that rely either on selectively permeable membranes or gas
absorbing beds of chemicals to separate the components of air from each
other. The membranes allow certain gases such as water vapor and oxygen
to pass through them rapidly, while the nitrogen will make it all the
way down the length of the membrane tube and be delivered in very high
purity. In 1998, the following four companies controlled over 50% of
the 30 billion dollar per year industrial gas business: Air Products
and Chemicals (United States), L'Air Liquide (France), The BOC Group
(United Kingdom) and Praxair, Inc. (United States).
And here are a few good links to get you started.
1. 2.
2. 3.
3. 4.
4.
This site is made possible by funding from the National Science Foundation (DUE-9981111).
|





