What is 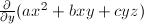 ?
?
- 0
- 2ax+b+c
- bx+cz
- by+cy
- b+c
Consider a 2d box which is infinite in one dimension and finite in the other. This is a reasonable model of quantum wells constructed by growing thin layers of different materials on a surface. What would you expect the energy levels to be like?
- They would be discrete, but more spread out than in a square box.
- They would be discrete, but closer together than in a square box.
- Any energy would be allowed.
- They would be the same as those in a square box.
- It depends on the depth and width of the box.
How would you expect the energy levels in a cube to compare with those in a square box if both had sides of the same length?
- They energies would be the same.
- The cube ground state energy would be higher.
- The cube ground state would have a higher degeneracy.
- The degeneracies would be the same.
- It's impossible to tell.
Consider the (2,1) state in a square box. What is the probability density of finding an electron in the center of the box?
- maximum
- zero
- positive, but less than the maximum
- negative, but more than the minimum
- It's impossible to tell.
Which of the following potential energies will result in a 3d Schrödinger equation which is separable into radial and angular parts?
- U=ar1/2 + e-r
- U = a/r cos(θ)
- U = r2 + 2r
- U = x/r + y/r
- U = a (constant)
The solutions to the θ and φ equations in the 3d radial Schrödinger equation will depend on the precise form of the central potential.
- True
- False
Two wave functions with different values of the absolute value of their angular momentum quantum number m but with the same value for the radial quantum number n will have the same radial shape.
- True
- False
Which radial wavefunction would you expect to have the most nodes? (A node is a place where the wave function is equal to 0.)
- n=1
- n=2
- n=3
- n=4
- n=5
How would the mean free path of hydrogen atoms in the n=3 state compare with the mean free path of hydrogen atoms in their ground state (n=1)? Assume the temperature and density are the same in both cases?
- same
- 9 times as big
- 9 times smaller
- 81 times as big
- 81 times smaller
Since the potential energy is spherically symmetric, how do we know which direction to take as the z direction?
- We don't. It's arbitrary.
- It is determined by the magnetic field of the nucleus.
- It depends on the spin of the electron.
- It depends on the orientation of the atom.
- It's determined by the right hand rule. Use your fingers to follow the orbit of the electron and your thumb will point in the z direction.
50. Which of the following are possible states in a hydrogen atom?
- 2p, m=0
- 1p, m=-1
- 3d, m=2
- 4s, m=-1
- 2s, m=1
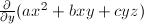 ?
?