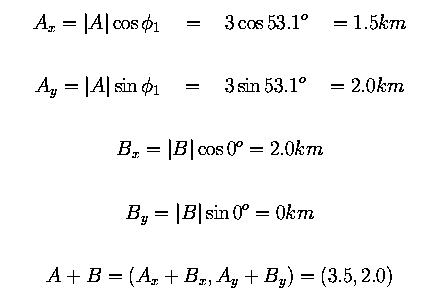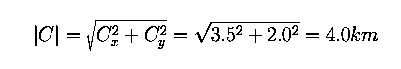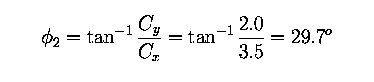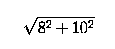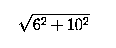Solutions to Scalar and Vector Problems
Solutions to Scalar and Vector Problems
Example 1
A hiker walks 53.1 degrees north of east for 2.5km then due east for 2.0km.
What is her total displacement from her starting point if you measure the
distance along a straight line?
The displacement is measured in distance and angle so we will compute both.
First, we draw a diagram of the hiker's path.
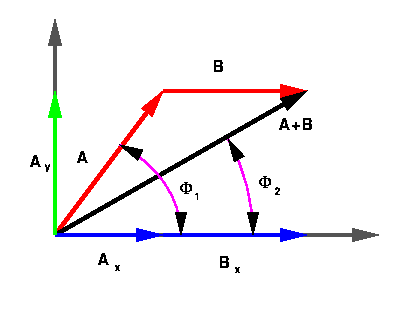
Let A be the first leg of the journey and B be the second.
What we are looking for is the vector A+B. We find that:
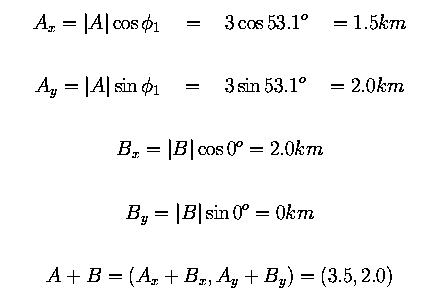
So the distance from the starting point is given by the pythagorean theorem:
(For convenience let C be the resultant vector.)
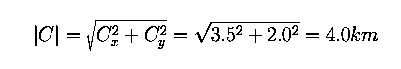
The angle of the resultant vector is:
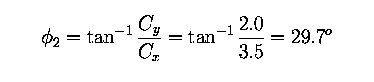
Example 2
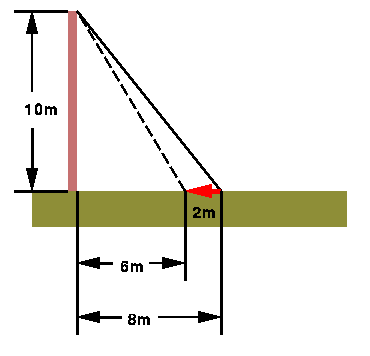
A telephone pole support cable is in the way of some construction workers.
In order for the work to proceed, the cable must be moved 2 meters closer to
the pole. If the pole is 10 meters tall and the cable is currently fastened
to the ground 8 meters from the pole, how much will the workers need to
cut off from the cable when they move it?
Again, we draw a diagram to help clarify the problem.
The original cable length is
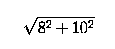 or 12.8m.
or 12.8m.
By moving the cable 2 meters closer to the pole, we shorten
the overall length of the cable to
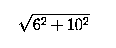 or 11.7m. Therefore, 1.1m must be cut off the cable.
or 11.7m. Therefore, 1.1m must be cut off the cable.
Click here to return to the vectors page.